Health By U.S. Gov Connect For Articles And Videos.
Neurogenesis
 Learn More
Learn MoreNeurogenesis is an extraordinary process through which the brain generates new neurons, or nerve cells. Once thought to occur only during embryonic development, research has uncovered that neurogenesis continues into adulthood, particularly in specific brain regions. This ongoing generation of neurons plays a crucial role in cognitive functions such as memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
For Health Treatment Monitoring and Scans And Hospitals
 Learn More
Learn MoreIn today's fast-paced world, technology has made remarkable advancements in the field of healthcare. From accurate diagnosis to efficient treatment monitoring, and state-of-the-art scanning techniques, technology has undoubtedly revolutionized the healthcare industry. This article delves into the various ways technology has enhanced health diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and the role of scans and hospitals.
What is Respiratory & Lungs System?
 Learn More
Learn MoreRespiratory is a term that refers to the system in our body responsible for the process of respiration, or breathing. It is a vital function that ensures the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide, allowing our body to function properly.
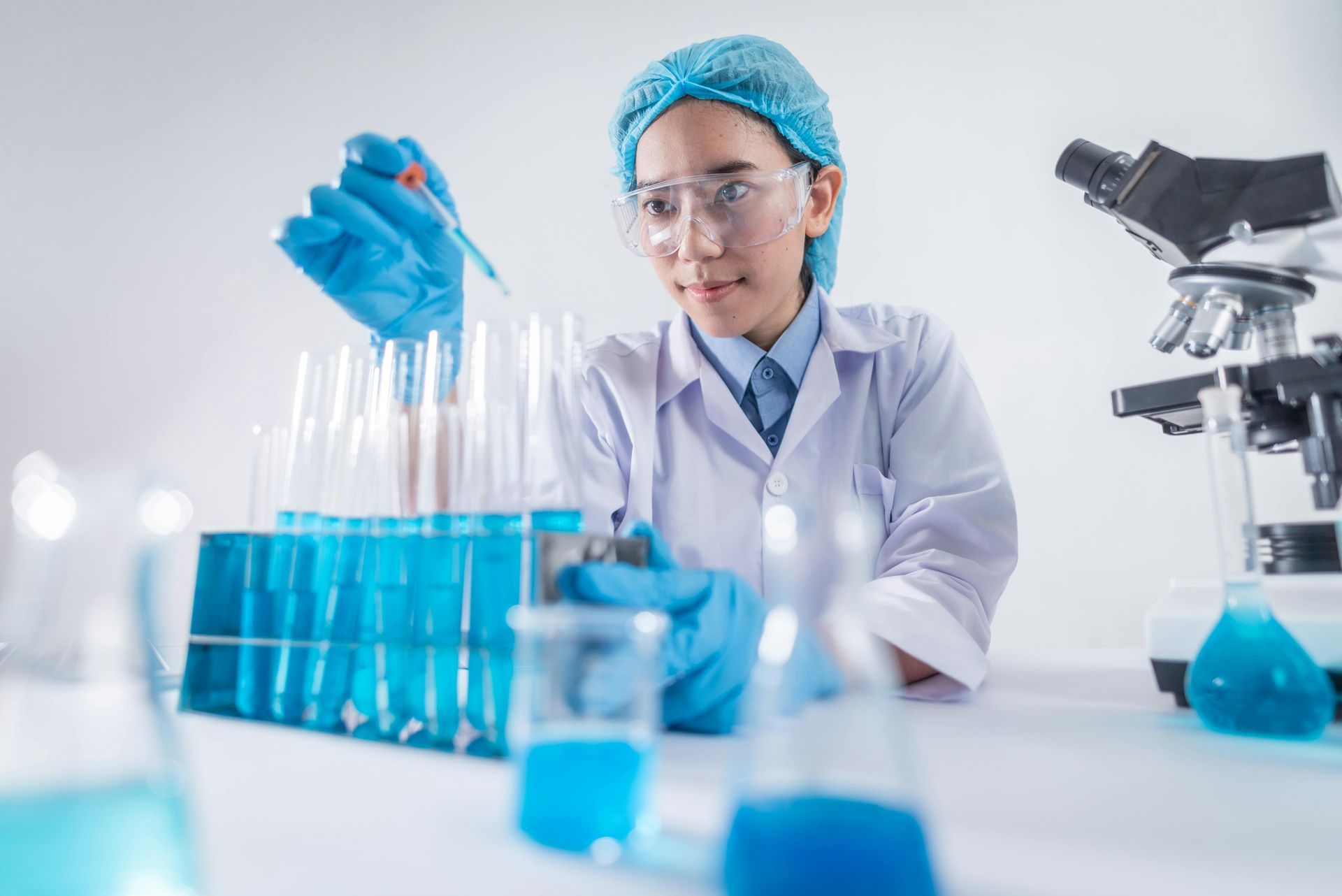
Pharmacy Drug Discovery And Developments
 Learn More
Learn MoreIn a world where new diseases and medical conditions arise constantly, the need for innovative pharmaceuticals has never been more crucial. Pharmacy drug discovery and developments play a vital role in providing effective treatments and improving the quality of life for countless individuals.
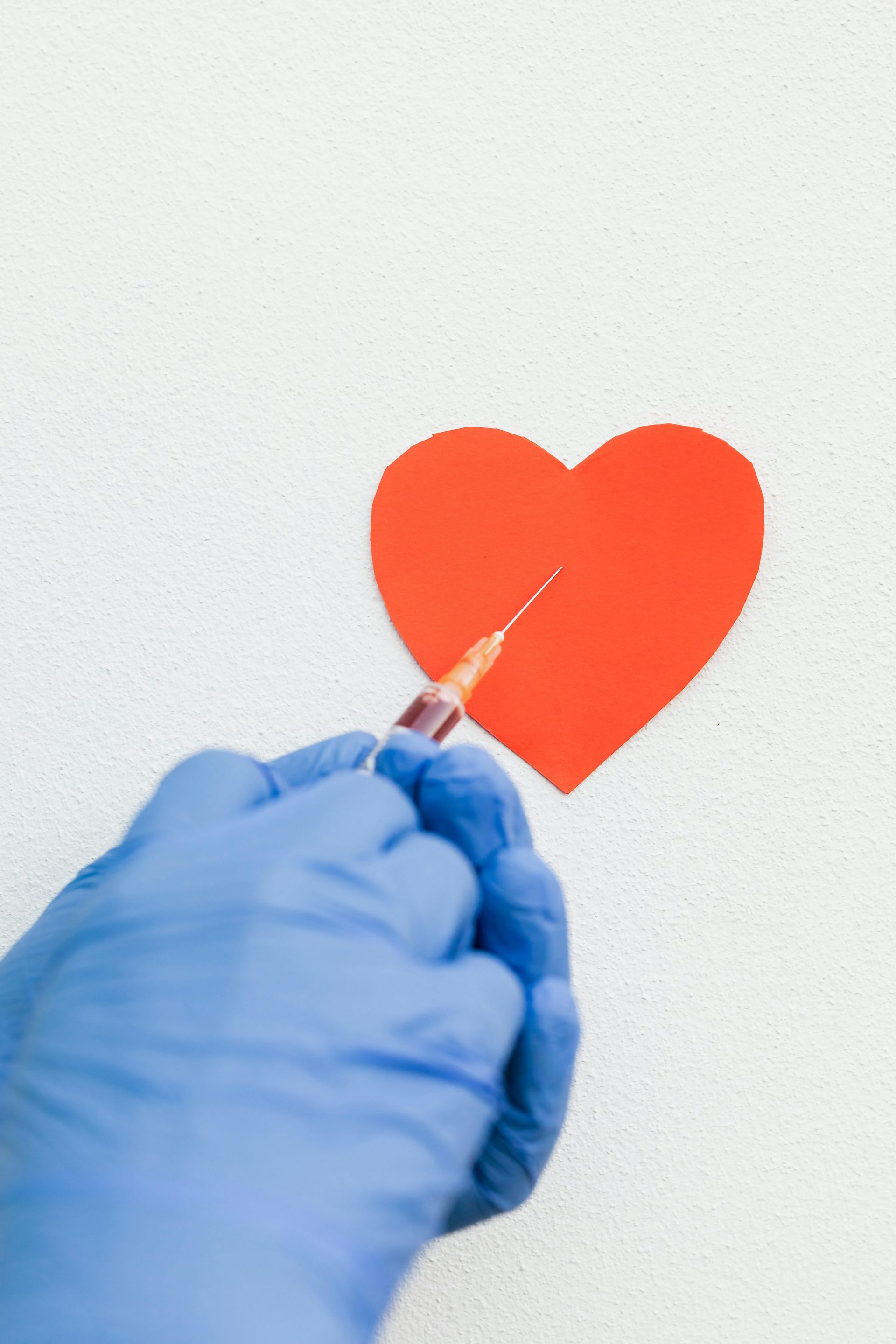
What is Cardiovascular Disease?
 Learn More
Learn MoreAs a cardiologist, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of various cardiovascular conditions, including strokes. A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain, leading to damage or death of brain cells. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention to minimize the long-term effects and increase the chances of survival.
Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment
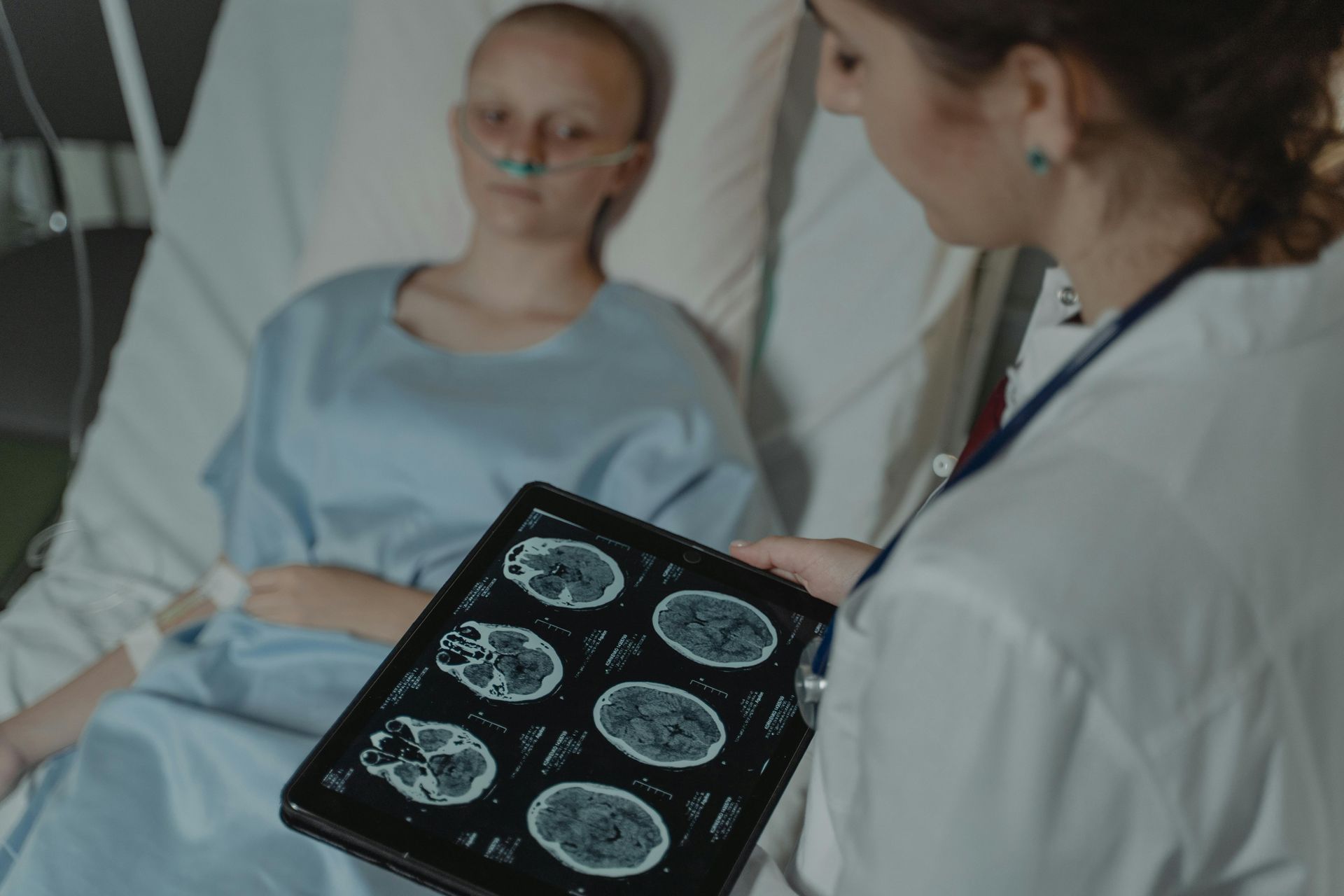 Learn More
Learn MoreCancer is a devastating disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Being diagnosed with cancer can be overwhelming and terrifying, but it's important to remember that there are numerous treatment options and resources available to help you on your journey to recovery. In this article, we will discuss the process of cancer diagnosis and the various treatment options available.
Neurology is the medical field that studies the nervous system
 Learn More
Learn MoreNeurogenesis is an extraordinary process through which the brain generates new neurons, or nerve cells. Once thought to occur only during embryonic development, research has uncovered that neurogenesis continues into adulthood, particularly in specific brain regions. This ongoing generation of neurons plays a crucial role in cognitive functions such as memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
Healthy Lifestyle
Describe the item or answer the question so that site visitors who are interested get more information. You can emphasize this text with bullets, italics or bold, and add links.Learn More
A Health Systems: Revolutionizing the Future of Medical Services
In the modern world, technology has revolutionized many industries, and the healthcare sector is no exception. One of the most exciting developments in healthcare is the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in providing health services. AI has the potential to transform the way healthcare is delivered and improve patient outcomes.
To understand the significance of AI in health services, let's begin by defining what AI is. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to learn, reason, and make decisions. In the healthcare field, AI can be used to analyze complex medical data, support diagnosis and treatment decisions, and even assist in surgery.
One of the main benefits of AI in health services is the ability to process and analyze vast amounts of medical data quickly and accurately. This data includes patient records, lab results, medical images, and research papers. AI algorithms can review this information at a much faster pace than human doctors, leading to more efficient and accurate diagnoses.
AI can also aid in personalized medicine. By analyzing a patient's medical history, genetic information, and lifestyle factors, AI algorithms can generate tailored treatment plans and recommendations. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and a more efficient use of resources.