Discover how climate change is reshaping Earth's ecosystem
Climate change is transforming habitats and driving species to adapt or face extinction. Learn about the impacts on biodiversity and what we can do to help!
Discover How Climate Change is Reshaping Earth's Ecosystem
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, profoundly affecting our planet's ecosystems. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the natural world is responding in ways that are both complex and alarming. Here are seven key ways climate change is reshaping Earth's ecosystems.
Altered Habitats
As temperatures change, many species are forced to migrate to cooler areas. This shift leads to alterations in habitats that can threaten the survival of various organisms. For example, polar bears are losing sea ice in the Arctic, which is critical for their hunting and reproduction. Meanwhile, tropical forests are experiencing shifts in species composition as climate zones change, which can disrupt delicate ecological balances.
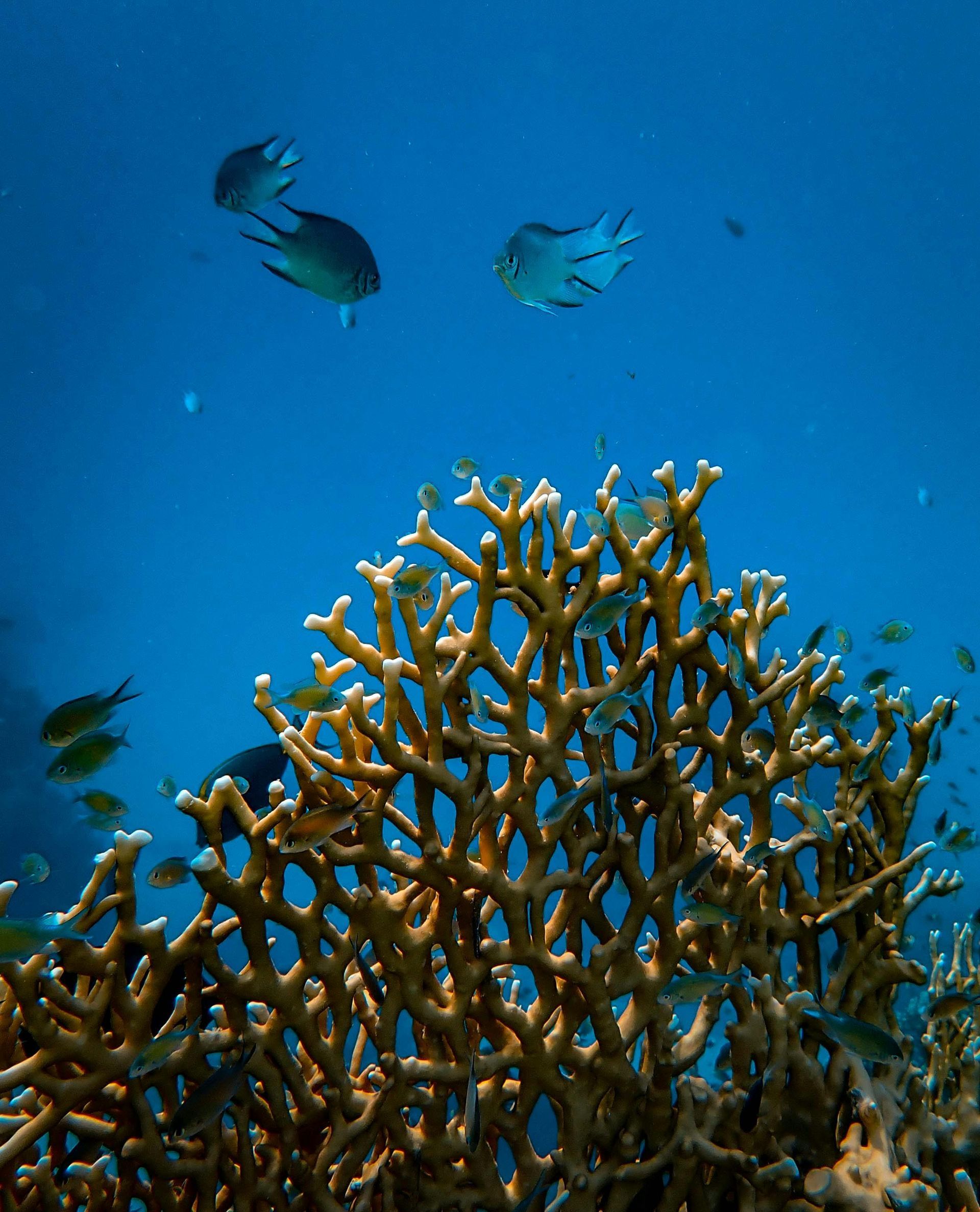
Ocean Acidification
The oceans absorb a significant amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere, leading to acidification. This change affects marine life, particularly species with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals and shellfish. Coral reefs, which support a vast diversity of marine life, are experiencing bleaching events and diminished growth, leading to a decline in marine biodiversity.
Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is linked to a rise in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. These events can have devastating impacts on ecosystems, leading to habitat destruction, loss of species, and increased stress on remaining wildlife. For instance, wildfires can alter landscapes, making it difficult for certain plants and animals to survive and recover.
Species Extinction
As ecosystems change, some species find it increasingly difficult to adapt to new conditions, leading to increased extinction rates. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) estimates that climate change could threaten more than 1 million species with extinction. The loss of biodiversity has ripple effects throughout ecosystems, affecting food webs and ecosystem services that humans rely on.
Shifts in Migration Patterns
Many animal species have specific migration patterns that are closely tied to seasonal cues. Climate change disrupts these patterns, causing species to migrate earlier or later than usual. For example, birds that rely on seasonal insects for food may arrive at their breeding grounds before their food source is available, leading to decreased reproductive success and population declines.
Changes in Plant Growth Cycle
Warmer temperatures and increased carbon dioxide levels are altering the growth cycles of plants. Many species are blooming earlier in the spring or changing their leaf-out times, which can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, if flowering plants bloom before pollinators emerge, it can disrupt plant-pollinator relationships critical for reproduction.
Soil Degradation
Climate change is exacerbating soil degradation through increased erosion, nutrient depletion, and disturbances caused by extreme weather events. Healthy soil is vital for plant growth and food production, as it supports the necessary microorganisms and nutrients. Soil degradation not only threatens agricultural sustainability but also reduces the ability of ecosystems to regenerate and sequester carbon, further fueling climate change.