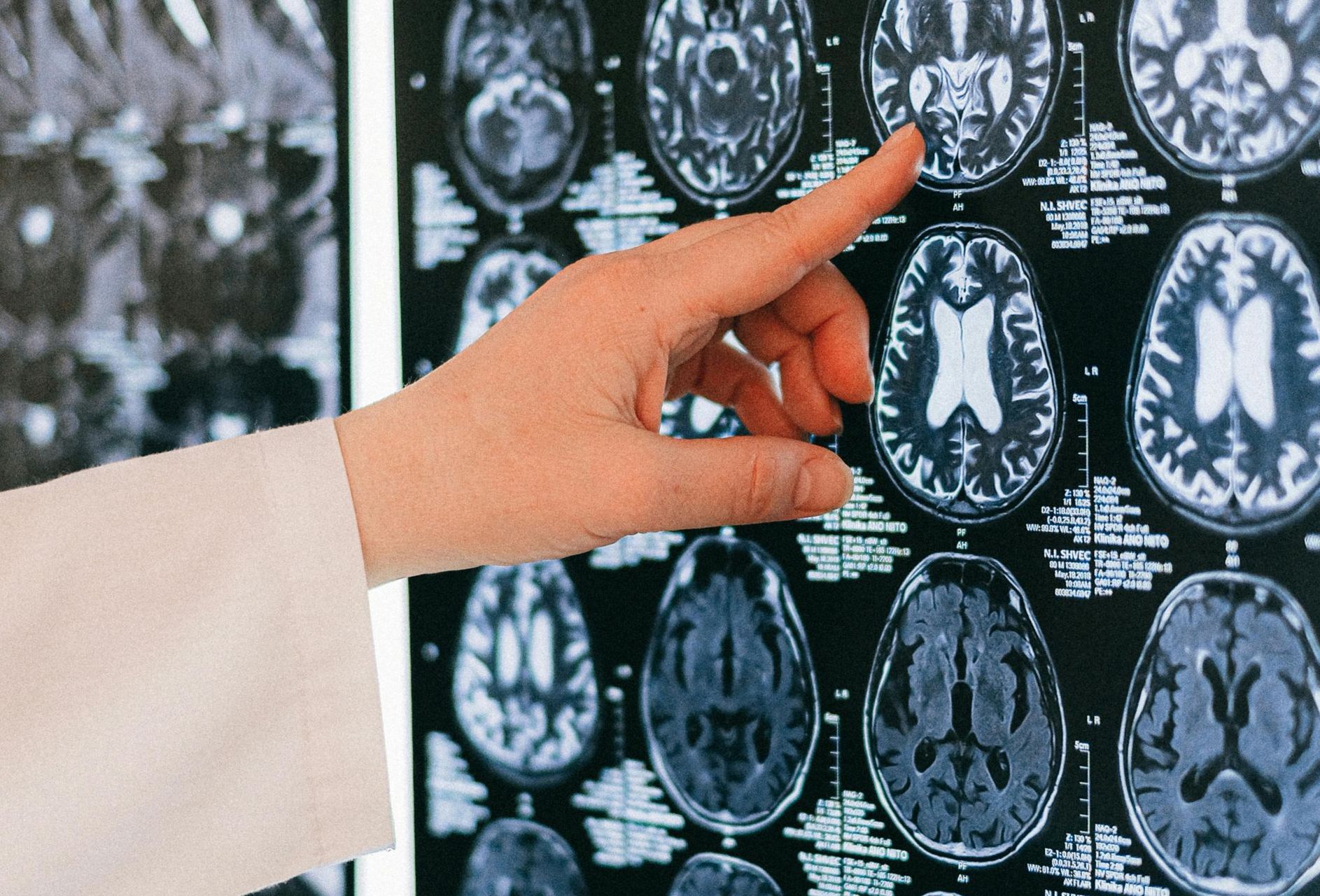
A blood clot is a gel-like mass that forms when blood components, such as platelets and fibrin, clump together. Under normal circumstances, blood clotting is a natural and necessary process that helps prevent excessive bleeding when the body is injured. However, when a clot develops in an artery supplying blood to the brain, it can disrupt the normal blood flow and deprive brain cells of the oxygen and nutrients they need to survive.
This condition, known as an arterial blockage or ischemic stroke, is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. The severity and lasting impact of an ischemic stroke depend on various factors, including the size of the blocked artery, the duration of the blockage, and the location of the clot within the brain. The longer the brain goes without proper blood flow, the more damage is likely to occur.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of an arterial blockage is crucial for prompt medical intervention. Common symptoms include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, loss of coordination, severe headache, and dizziness. If you or someone around you experiences any of these symptoms, it is essential to call emergency services immediately.
Medical professionals utilize various techniques to diagnose and treat arterial blockages in the brain. Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can help identify the location and extent of the clot. In some cases, medication may be administered to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow, a procedure known as thrombolysis. Alternatively, surgical interventions, such as a mechanical thrombectomy, may be necessary to physically remove the clot from the affected artery.
Prevention is always better than cure, and reducing the risk of arterial blockages in the brain is no exception. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco use can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing blood clots. Additionally, managing chronic conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can further minimize the risk of arterial blockages.
In conclusion, an arterial blockage caused by a blood clot in the brain is a serious medical condition that demands immediate attention. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical care can improve the chances of a successful treatment outcome. Remember, prevention is key, so take proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage any underlying health conditions. Your brain will thank you for it.